Neuromorphic Benchmarking
Neuromorphic Processing Element Array
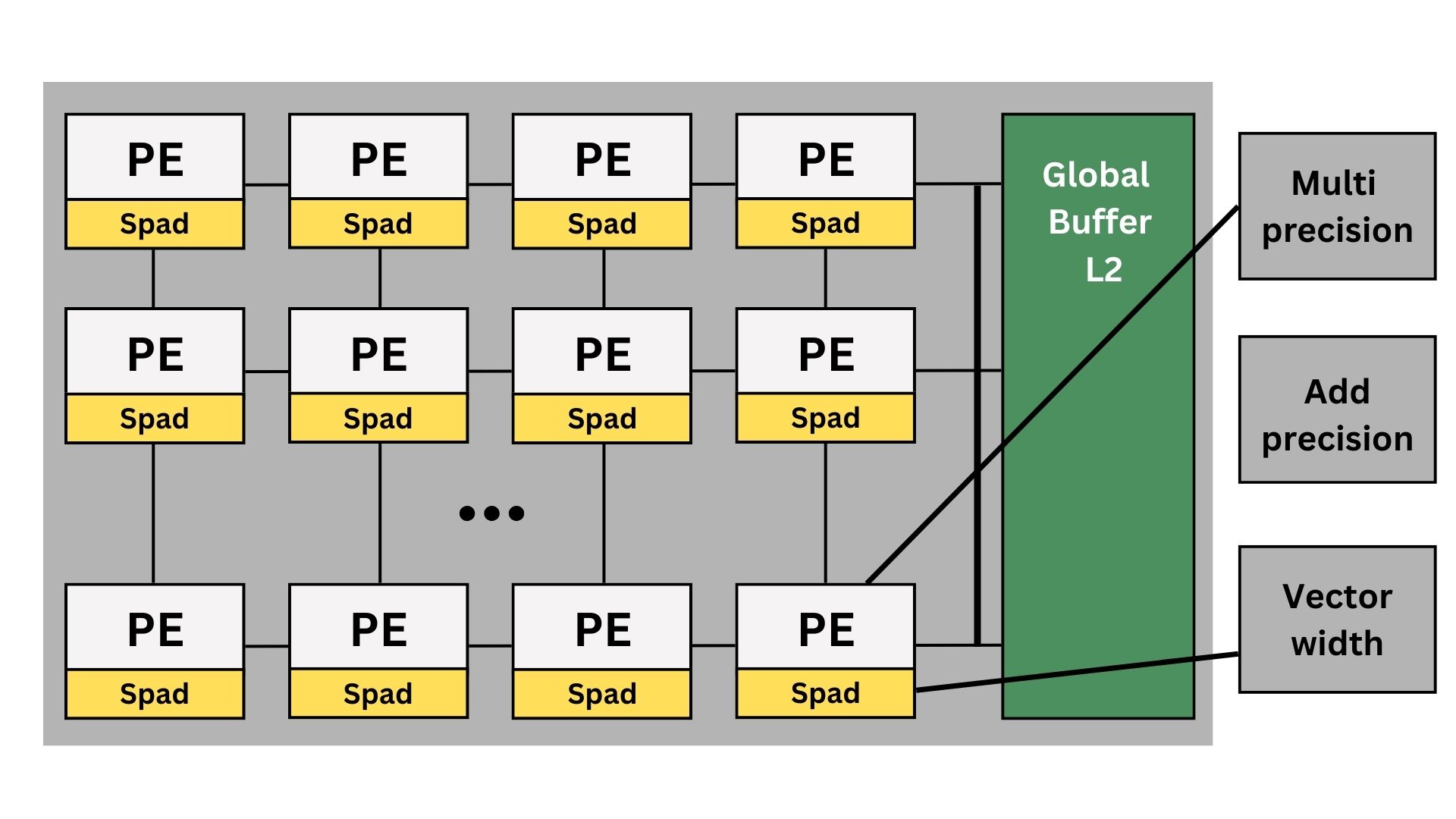
The AI accelerator is built around a 2-D mesh of identical processing elements (PEs), each pairing an L1 Spad SRAM with a tunable arithmetic pipeline whose multiplier bit-width, adder bit-width, and vector length can be set per workload. PEs exchange data over short, pipelined links across the mesh, while a centrally positioned, multi-ported L2-class global buffer streams weights and feature maps to the array and gathers partial results. This tiered memory hierarchy—private L1 Spad for high-reuse data and a shared L2 for larger tensors—minimizes off-chip traffic and lets the accelerator scale smoothly from energy-efficient INT8 inference to higher-precision operations simply by retargeting the per-PE arithmetic parameters without altering the mesh fabric or software stack.We also optimize dataflow and throughput by clustering multiple processing element during model compilation time.[More detailed models]
| Neuromorphic workload | Input resolution/sequence length | Latency(ms) | Throughput(FPS) | Area(mm²) | $ per token | Throughput(token/sec) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mobilenet v2 [1] | 224 x 224 x 3 | 10 | 1328 | 907.69 | ||
| GEMM [1] | 224 x 224 x 3 | 3929 | 3.101 | 907.69 | ||
| Mnasnet [1] | 224 x 224 x 3 | 32.2 | 332.16 | 907.76 | ||
| Resnext50 [1] | 224 x 224 x 3 | 1480 | 6.811 | 907.76 | ||
| squeezenet [1] | 224 x 224 x 3 | 34.4 | 116.89 | 907.76 | ||
| Transformer [1] | 224 x 224 x 3 | 9.5 | 6150 | 907.76 | ||
| unet [1] | 224 x 224 x 3 | 3286 | 2.23 | 907.6 | ||
| Vgg16 [1] | 224 x 224 x 3 | 121 | 63.4 | 907.76 | ||
| BERT-L [2] | 128/128 | 3.7 seconds | 806.89 | |||
| Llama 3.2_1B [3] | 512/512 | 907.6 | 1400 |
